Assessment of Roundup® cardiotoxicity on guinea-pig isolated Langendorff perfused heart and human lnduced Pluripotent Stem Cells derived cardiomyocytes
R. Printemps, S. Guilbot, H. Didier, M. Le Grand, PhysioStim, Zone Industrielle de Brénas, 81440 Lautrec, France
Although pesticides are known to be the key actors of modern agriculture, they are source of controversies due to their suspected hazardous health effects. Roundup®, one of the most popularized pesticide, is composed of Glyphosate, its active ingredient, and adjuvants. The broad use of Roundup® through the years in agricultural practices as well as home garden care led to large exposure of humans and mammalians to Glyphosate.
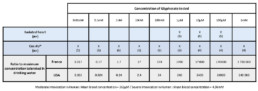
Many pesticides such as Glyphosate persist in soils and water so that human exposure can be important even to those who do not use it. ln France, the Maximum Contamination Level (MCL) authorized in drinking water is 0.1 ng/ml (=0.59nM) while in USA, EPA authorized concentration up to 0.7ng/ml (=4.lnM). Acute intoxication after ingesting Glyphosate are also observed in suicidai or accidentai cases leading to mean blood concentration ranging from 61µg/ml (=361µM) considered as moderate intoxication to 838µg/ml (=4.96mM) considered as severe intoxication.A number of severe clinical outcomes have been reported: nausea, vomiting, ulceration, acidosis, respiratory distress, impaired renal function, hepatic toxicity, haemodynamic disturbance, cardiac arrhythmia. The purpose of this work was to examine the effects of Roundup® exposition on heart function using Langendorff isolated guinea-pig (GP) perfused heart and human lnduced Pluripotent Stem Cells derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CM) models.
Methods
lsolated Langendorff-perfused guinea pig heart preparations
- Spontaneous beating Langendorff isolated perfused hearts from male guinea-pig were perfused with Krebs' solution, oxygenated and warmed at 37 + 1 °C, at a constant perfusion pressure of 55 + 5 mm Hg.
- After an equilibration period and a 10 min contrai perfusion, three concentrations of Glyphosate (see table 1) were perfused during 20 min each.
- The following parameters were measured: left ventricular pressure (LVP), maximal contraction velocity (Max dP/dt) and maximal relaxation velocity (Min dP/dt), heart rate (HR), coronary flow (CF) and ECG parameters (PR, RR, QRS, QT and QTc (Fridericia) intervals)
Hum an lnduced Pluripotent Stem cells derived cardiomyocytes
- Cor.4U® Cardiomyocytes were supplied by Ncardia and seeded on 48 wells plate following manufacturers instruction and analyzed using the xCELLigence RTCA cardia ECR platform (simultaneous measurement of MEA and impedance).
- 4 to 5 days after seeding, Cor.4U® cardiomyocytes were exposed during 18h to 24h to different concentrations of Roundup (up to 9 concentrations, see table 1, only some of them are presented in the result section).
- The following parameters were monitored: Cell Index (Cl), Amplitude of contraction, Beat rate, Beating period, lndividual Beating Duration (IBD), Field Potential Duration (FPD) and FPD corrected by Fridericia (FPDc), Spike amplitude, Beating Rhythm lrregularity (BRI).
Compound administration
Roundup® was diluted in distilled water and the combine effects of Glyphosate and adjuvants were evaluated. Concentration of Roundup® tested have been expressed as Glyphosate concentration.
Results
Guinea pig heart preparation
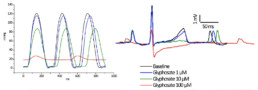

- No effect of Glyphosate at 1µM
- No effect of Glyphosate at 10µM on ECG parameters but , ↗ CF (+39%) and ↘ LVP (-26%)
- At lOOµM, Glyphosate ↘ HR (-33%), LVP (-92%) and CF (-43%) and , ↗ all ECG parameters (RR +50%, PR +39%, QRS +58% and QTc +28%). AV Black was observed in 1 of 5 preparations.
Cor.4U ® cardiomyocytes
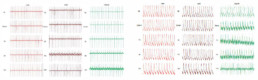
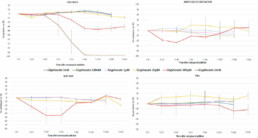
- No effect of Glyphosate from 0.01n M to lµM on viability, contractility and electrical activity.
- At lOµM, Glyphosate had no effect on Cell index and contractility but ,↗ FPDc (+15%).
- Glyphosate induced ↘ Cell Index with time at 100µM (-35% after 6h), ↘ amplitude of contraction and beat rate (maximum effect -48% and -45% after 6h respectively) but no modification of FPDc before 18h exposition.
- With Glyphosate lmM, Cor.4U® cardiomyocytes stopped beating after 5min exposition and Cell Index ↘ up to -97% after 6h corresponding to cardiomyocytes death.
conclusion
- Evaluation of the global effects of Roundup® (Glyphosate + adjuvants).
- Bath models were able to detect cardiotoxicity of Roundup® mainly characterized by a massive decrease of the heart's contractile function and troubles in electrical conduction.
- Effects observed in man after Roundup® intoxication, as reported in the literature (moderate ≈ 360µM to severe intoxication ≈ 5mM), were consistent with those observed in these in vitro - ex vivo models.
- These predictive and sensitive assays are particularly relevant for cardiotoxicity assessment of pesticides but also to many other compounds produced by chemicals and fine chemicals industries.
Please fill out the form below to receive the poster