Cardiac toxicity comparison of Roundup® and glyphosate on human Induced Pluripotent Stem cells derived cardiomyocytes
Printemps R, GuilbotS, Le Grand M, PhysioStim, Zone Industriellede Brénas, 81440 Lautrec, France.
Although pesticides are known to be key actors of modern agriculture,they are source of controversies due to their suspected hazardous health effects.
Roundup®, one of the most popularized pesticide, is an herbicide formulation based on an active ingredient, glyphosate, and adjuvants. The broad use of Roundup® through they ears in agricultural practices as well as home garden care led to large exposure of humans and mammalians to glyphosate. Evaluation of the safety and potential health risks from exposure to pesticides remains a major challenge.
Roundup® and glyphosate were compared using human cell based model to evaluate their impacts on cardiovascular function after exposition.
Materials and Methods
- iCell® Cardiomyocytes2 were supplied by Cellular Dynamics (a Fujifilm company) and seeded on 48 well plate following manufacturers instruction and analyzed using the xCELLigence RTCA cardio ECR platform (simultaneous measurement of MEA and impedance).
- 4 days after seeding, iCell2 cardiomyocytes were exposed during 24h to 5 different concentrations of Roundup® or glyphosate(from 0.01 to 100μM) prepared from stock solutions diluted in distilled water(final concentration of distilled water was 0.3%).
- Roundup® solution used during this study is composed of 400g/L of glyphosate. Concentration of Roundup® presented here after correspond to the concentration of glyphosate present in the solution (Roundup® 10μM correspond to 10μM of glyphosate)
- Data are expressed as Mean ± SD. Each concentration of compound was administrated in 4 wells.
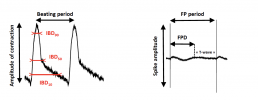
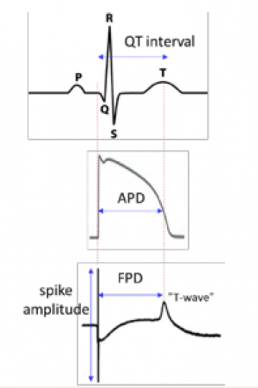
- The following parameters were monitored: Cell Index (CI), Amplitude of contraction, Beat rate (BR),Beating period(BP),Individual Beating Duration(IBD),Field Potential Duration(FPD) and FPD corrected by Fridericia(FPDc),Spike amplitude,Beating Rhythm Irregularity (BRI).
Results
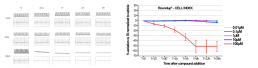
Roundup®
Glyphosate
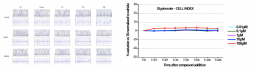

- No effect of glyphosate from 0.01 μM to 100 μM on viability, contractility and electrical activity.
- Roundup® up to 10 μM had no effect on viability and electrical activity, only as light decrease of amplitude of contraction was recorded (-11%) after 6 hand sustained within 24h at 10μM.
- iPSC-CMs stopped beating during Roundup® 100μM.
conclusion
- The absence of effects of glyphosate on cardiac function indicates that the cardiotoxicity observed with Roundup®could be attributed to Roundup®’sadjuvants.
- This predictive and sensitive assay can be very useful for cardiotoxicity assessment of pesticides using a human cell based model. This work demonstrates that the evaluation of pesticides’ adjuvants is necessary to better address the safety of pesticides which can also be enlarged to a broader class of molecules.
Please fill out the form below to receive the poster