CaV1.2 assays

Cardiac Calcium channel (CaV1.2)
The voltage gated cardiac calcium channel Cav1.2, encoded by the CACNA1C gene, is a key component of the plateau phase and is highly implicated in the depolarization process of the action potential. When the calcium channel is activated or with a delayed inactivation some undesirable cardiovascular side effects could be induce leading to life threatening arrhythmias called Torsade de Pointes. When the calcium channel is blocked some worsening of the cardiac contractility could be induced.
CaV1.2 assay & preclinical studies
Cav1.2 channel assays aim to identify potential blocking effects early in the drug discovery phase. some clinically successful drugs have been reported to delay the inactivation of the calcium channel, are known to increase the risk of sudden death. Furthermore, drug that induce Cav1.2 blockade might be documented in order to anticipate their hemodynamic effect.
What is the added value of such a study?
- Anticipation of cardiac hemodynamic effects
- Threshold concentration of Cav1.2 blockade
- Leading to the determination of the safety range versus efficacious concentration
- You obtain your safety margin
Automated Patch Clamp
Technique
- Human Embryonic Kidney HEK-293 cells
- Experiment conducted at room temperature or at physiological temperature (35°C)
- Up to 6 increasing cumulative concentrations of test compound or biologic.
Measured parameters
- Amplitude of the peak current upon depolarization to 0 mV (pA)
- Amplitude of the base current at –80 mV (pA)
- Ion current amplitude measurement
- Inhibition of Cav1.2 peak current amplitude (%)
- IC50 value (at least 4 concentrations required)
Main advantages
- High throughput screening
- Cost effective
- Fast process to delivery results
- Perfect at earliest stages
- Design protocol could be adapted
Manual Patch Clamp
Technique
- Human Embryonic Kidney HEK-293 cells
- Experiment conducted at room temperature or at physiological temperature (35°C)
- Up to 5 increasing concentrations of test compound tested independently
- At least 3 treated cells are recommended
Measured parameters
- Amplitude of the peak current upon depolarization to 0 mV (pA)
- Amplitude of the base current at –80 mV (pA)
- Ion current amplitude measurement
- Inhibition of Cav1.2 peak current amplitude (%)
- IC50 value (at least 4 concentrations required)
Main advantages
- Technically robust
- Highly informative (more accurate IC50 value)
- Strongly replicable
- Design protocol could be adapted
Manual Patch Clamp - GLP Conditions
Technique
- Human Embryonic Kidney HEK-293 cells
- Experiment conducted at room temperature or at physiological temperature (35°C)
- At least 4 increasing concentrations of test compound tested independently
- At least 5 treated cells is highly recommended for a regulatory application
- Vehicle group is also highly recommended
- Sampling pre- and post- perfusion for analytical quantification
Measured parameters
- Amplitude of the peak current upon depolarization to 0 mV (pA)
- Amplitude of the base current at –80 mV (pA)
- Ion current amplitude measurement
- Inhibition of Cav1.2 peak current amplitude (%)
- IC50 value
Main advantages
- Technically robust
- Highly informative (more accurate IC50 value)
- Strongly replicable
- Design protocol could be adapted
- Sampling
- Analytical quantification under GLP conditions (also mandatory) could be performed by the Sponsor or with PhysioStim
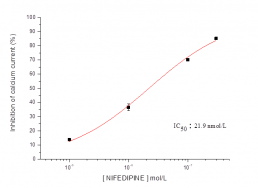
Typical concentration dependent effects of nifedipine on Cav1.2 current recorded from HEK-293 cells.
Reference compounds or positive controls
Reference CompoundsIC₅₀
Verapamil3.4 µM
Nifedipine21.9 nM
Diltiazem7.7 µM