Vascular Pharmacology

Vascular Pharmacology in organ baths
Whatever the therapeutic area, some compounds through their targets or off-targets could modulate the vascular hemodynamic. That is why we perform secondary pharmacology (targets or off-targets dependent) by using the isolated organ baths under normal or diseased conditions. Therefore, vasodilator and vaconstrictor effects induced by drugs are investigated with well established mediators (voltage and non-voltage dependent). Ring strips of various vessels, in presence or absence of endothelium function (mimicking shear stress or arterosclerotic conditions), are mounted in the organ baths chambers. The variation of tension representative of variation of blood pressure is recorded using a force transducer.
Vascular assays & secondary pharmacology
Vascular assays aim to identify potential hemodynamic effects (hypertensive or hypotensive blood pressure) early during drug development. Numerous clinically approved drugs reported to induce hypertension increasing the risk of vascular failures (stroke, myocardium infarction, lower limbs ischemia and claudication). As a result, a large number of drugs have been contraindicated with the use during late stage of clinical trials or from the market.
What is the added value of such a study?
- Strongly recommended for the secondary pharmacology of regulatory documents
- Threshold concentration of the target and off-target vascular reactivity
- Prediction of the effect on blood pressure
- Determination of appropriate In Vivo model
Organ baths
Technique
- Isolated organ baths system
- Aortic rings (Rat, Guinea-pig, rabbit, mouse)
- In absence or presence of endothelium
- Upon request: Ring strips from artery or vein
- 4 preparations tested and 4 control preparations (as basic design protocol but can be adapted)
Measured parameters
- Variation of tension
- Upon request: Biomarkers assays
Main advantages
- Medium throughput screening
- Cost effective previous In Vivo model
- Fast process to delivery results
- Perfect at earliest stages
- Highly predictible
- Design protocol could be adapted
Experimental conditions
Experimental conditions
VasoconstrictorsPhenylephrine • Endothelin • Serotonin • KCl
VasodilatorsAcetylcholine • Substance P
Endothelium
FunctionEndothelium removed by rubbing the inner surface
NO synthase activity by incubation with L-Name
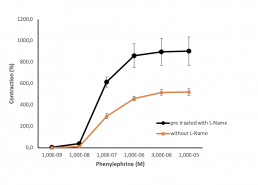
Concentration response curve with phenylephrine in the presence or absence of L-Name
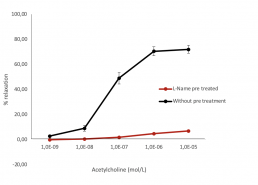
Concentration response curve with acetylcholine in the presence or absence of L-Name